The vestibular nerve, a crucial component of the inner ear, plays a vital role in our ability to maintain balance and perceive sound. When this intricate system becomes impaired, it can lead to a range of symptoms that may significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of vestibular nerve damage, from its anatomy and function to the identification of damage, symptoms associated with it, treatment options, and strategies for living with this condition.
Understanding the Vestibular Nerve
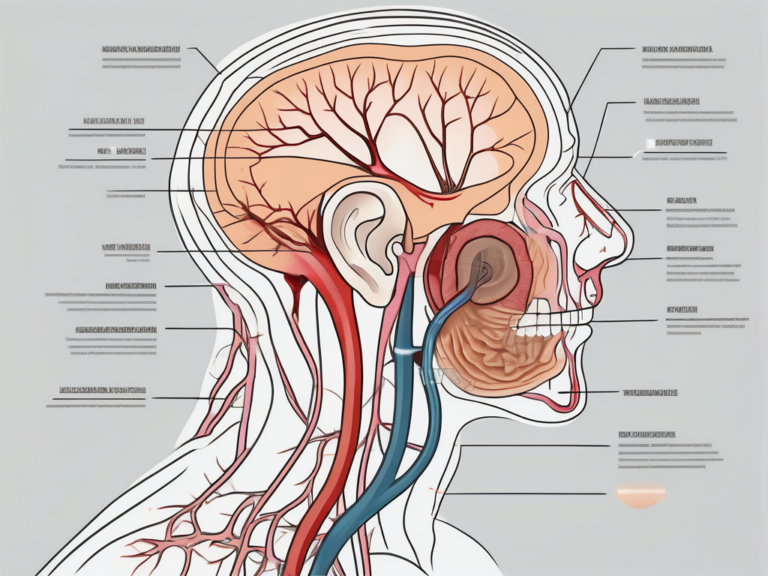
The vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve or the acoustic-vestibular nerve, consists of two components: the superior vestibular nerve and the inferior vestibular nerve. These nerves transmit signals from the inner ear’s vestibular organs to the brain, providing crucial information about our head position, movement, and spatial orientation.
The vestibular nerve plays a vital role in our daily lives, allowing us to navigate the world with ease and grace. Without this intricate system, simple tasks such as walking, running, and even standing upright would be incredibly challenging. Let’s delve deeper into the fascinating anatomy and function of the vestibular nerve.
Anatomy and Function of the Vestibular Nerve
The vestibular nerve is intertwined within the labyrinth of the inner ear, consisting of the semicircular canals and the otolith organs. These structures work together harmoniously to provide us with a comprehensive understanding of our body’s position in space.
The semicircular canals, three fluid-filled loops positioned at right angles to each other, detect rotational movements. When we turn our head or change our body’s orientation, the fluid inside these canals moves, stimulating tiny hair-like cells that line the canals. These hair cells convert the fluid movement into electrical signals, which are then transmitted through the vestibular nerve to the brain.
On the other hand, the otolith organs, consisting of the utricle and saccule, detect linear acceleration and gravity. They are filled with tiny crystals called otoliths, which shift in response to changes in head position or movement. Similar to the semicircular canals, the movement of these otoliths triggers the hair cells, generating electrical signals that travel through the vestibular nerve to the brain.
Together, the semicircular canals and otolith organs form a complex system that helps us maintain balance and coordination. They work in tandem with our visual system and proprioception (the sense of body position) to provide us with a comprehensive understanding of our body’s position in space.
Role of the Vestibular Nerve in Balance and Hearing
Aside from contributing to balance, the vestibular nerve is also responsible for relaying sound information from the ear to the brain. It works in harmony with the cochlear nerve, another component of the eighth cranial nerve, to ensure proper auditory perception.
The cochlear nerve is primarily responsible for transmitting sound signals from the cochlea, the spiral-shaped structure in the inner ear, to the brain. The vestibular nerve, however, plays a supporting role in this process. It helps to modulate our perception of sound by providing information about head movements and orientation, allowing us to better understand the auditory environment around us.
Furthermore, the vestibular nerve and the cochlear nerve share a common pathway as they travel from the inner ear to the brainstem. This close proximity allows for efficient communication between the two nerves, ensuring that our hearing and balance systems work seamlessly together.
In conclusion, the vestibular nerve is a remarkable component of our sensory system, enabling us to maintain balance, coordinate movements, and perceive sound accurately. Its intricate anatomy and function highlight the complexity of the human body and the remarkable ways in which it adapts to its surroundings.
Identifying Damage to the Vestibular Nerve
The vestibular nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining our sense of balance and spatial orientation. When this nerve is damaged, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including dizziness, vertigo, and problems with coordination. Identifying and understanding the causes of vestibular nerve damage is essential in order to provide appropriate treatment and management strategies.
Common Causes of Vestibular Nerve Damage
Vestibular nerve damage can occur due to various factors, each with its own unique impact on the nerve’s function. One common cause of damage is viral infections. Viruses such as the herpes simplex virus and the Epstein-Barr virus can invade the vestibular nerve, leading to inflammation and subsequent damage.
Head injuries are another significant cause of vestibular nerve damage. Traumatic events such as falls, car accidents, or sports-related injuries can result in direct trauma to the head, affecting the delicate structures of the inner ear, including the vestibular nerve.
Certain medications have also been associated with vestibular nerve damage. Ototoxic drugs, such as certain antibiotics and chemotherapy agents, can have a toxic effect on the nerve, leading to impaired function.
Age-related degeneration is another factor that can contribute to vestibular nerve damage. As we age, the structures of the inner ear naturally undergo changes, including a gradual decline in the number of nerve cells. This degeneration can affect the transmission of signals from the vestibular nerve to the brain, resulting in balance problems.
Infections such as vestibular neuritis and labyrinthitis are common culprits when it comes to vestibular nerve damage. These conditions typically arise from viral or bacterial infections that cause inflammation and damage to the vestibular nerve. Vestibular neuritis specifically affects the vestibular nerve, while labyrinthitis involves both the vestibular nerve and the cochlear nerve, which is responsible for hearing.
Diagnostic Procedures for Vestibular Nerve Damage
Diagnosing vestibular nerve damage often involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, a physical examination, and specialized tests. Understanding the extent and nature of the damage is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
During the medical history assessment, the healthcare provider will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, their duration, and any potential triggers. This information can provide valuable insights into the possible causes of vestibular nerve damage.
A physical examination may involve assessing the patient’s balance, coordination, and eye movements. Abnormalities in these areas can indicate dysfunction of the vestibular nerve. Additionally, the healthcare provider may perform specific tests, such as the Romberg test, which evaluates the patient’s ability to maintain balance with their eyes closed.
Specialized tests, such as electronystagmography (ENG) and videonystagmography (VNG), can provide further insights into the integrity of the vestibular nerve. These tests involve monitoring eye movements in response to various stimuli, such as changes in head position or visual cues. By analyzing these eye movements, healthcare providers can assess the function of the vestibular nerve and identify any abnormalities.
In some cases, additional imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be ordered to rule out other potential causes of the patient’s symptoms and to obtain a more detailed view of the inner ear structures.
Overall, the identification and diagnosis of vestibular nerve damage require a comprehensive approach that combines medical history assessment, physical examination, and specialized tests. By understanding the underlying causes and extent of the damage, healthcare providers can develop personalized treatment plans to help patients manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Symptoms Associated with Vestibular Nerve Damage
Vestibular nerve damage can have a profound impact on an individual’s physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being. The symptoms associated with this condition are varied and can significantly disrupt daily life.
Physical Symptoms of Vestibular Nerve Damage
One of the primary physical symptoms experienced by individuals with vestibular nerve damage is persistent dizziness. This sensation of spinning or lightheadedness can be debilitating, making it difficult to perform even simple tasks. Alongside dizziness, many individuals also experience vertigo, a false sense of movement that can cause a spinning or tilting sensation.
Imbalance is another common physical symptom of vestibular nerve damage. This can manifest as difficulty walking in a straight line or maintaining stability while standing. Coordination problems may also arise, making it challenging to perform activities that require precise movements.
In addition to these physical symptoms, individuals with vestibular nerve damage may also experience nausea and vomiting. These symptoms often accompany dizziness and vertigo, further complicating daily routines and making it difficult to engage in normal activities.
Cognitive and Emotional Impacts of Vestibular Nerve Damage
Vestibular nerve damage not only affects an individual’s physical well-being but also has cognitive and emotional implications. The constant battle with dizziness and imbalance can lead to increased levels of anxiety and stress. The fear of falling or losing control can be overwhelming, causing individuals to limit their activities and social interactions.
Depression is also a common emotional impact of vestibular nerve damage. The constant struggle with symptoms and the limitations they impose can lead to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a decreased overall quality of life. The loss of independence and the inability to participate in activities that were once enjoyed can further contribute to feelings of isolation and despair.
Cognitive difficulties are another consequence of vestibular nerve damage. Concentration problems and memory lapses can make it challenging to perform tasks that require focus and attention. The constant presence of dizziness and vertigo can be mentally exhausting, leading to fatigue and decreased cognitive function.
In conclusion, vestibular nerve damage can have a wide range of physical, cognitive, and emotional symptoms. The impact of these symptoms on an individual’s daily life can be significant, affecting their ability to perform routine tasks, engage in social activities, and maintain overall well-being. It is important for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek medical attention and explore treatment options to manage and alleviate the effects of vestibular nerve damage.
Treatment Options for Vestibular Nerve Damage
Medical Interventions for Vestibular Nerve Damage
The management of vestibular nerve damage often involves a multidisciplinary approach. Medications, such as anti-vertigo drugs and anti-nausea medications, may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms. These medications work by targeting the underlying causes of vestibular dysfunction, helping to restore balance and reduce dizziness. Anti-vertigo drugs, such as meclizine or betahistine, can help control vertigo episodes, while anti-nausea medications like ondansetron or promethazine can alleviate nausea and vomiting.
In more severe cases of vestibular nerve damage, surgical interventions may be considered. Vestibular nerve section, a procedure where the vestibular nerve is cut, can be performed to eliminate the signals causing vertigo. This surgery is typically reserved for patients who have not responded to other treatment options. Another surgical option is cochlear implants, which can help improve hearing in individuals with both vestibular nerve damage and hearing loss.
It is essential to consult with a medical professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for vestibular nerve damage. They will consider the severity of the condition, the individual’s overall health, and their specific symptoms before recommending the most suitable interventions.
Rehabilitation and Therapy for Vestibular Nerve Damage
Physical therapy and vestibular rehabilitation can play a crucial role in managing the consequences of vestibular nerve damage. These interventions aim to improve balance, reduce symptoms, and enhance daily functioning. Vestibular rehabilitation is a specialized form of physical therapy that focuses on exercises and techniques to promote adaptation and compensation for the damaged vestibular system.
During vestibular rehabilitation, trained therapists work closely with patients to develop a personalized treatment plan. They assess the individual’s specific impairments and design exercises to address their unique needs. These exercises may include gaze stabilization exercises, balance training, and habituation exercises to reduce sensitivity to motion.
Gaze stabilization exercises involve focusing on a stationary object while moving the head, which helps train the brain to process visual information accurately during head movements. Balance training exercises aim to improve stability and reduce the risk of falls by challenging the vestibular system and strengthening the muscles involved in balance control. Habituation exercises expose patients to specific movements or situations that trigger their symptoms, gradually desensitizing their response over time.
By implementing exercises tailored to an individual’s specific needs, trained therapists can help patients regain stability and confidence. Vestibular rehabilitation is typically a long-term process, and the duration of treatment varies depending on the severity of the vestibular nerve damage and the individual’s progress.
In addition to physical therapy and vestibular rehabilitation, other complementary therapies may also be beneficial for managing vestibular nerve damage. These can include acupuncture, yoga, tai chi, and mindfulness techniques. These practices can help reduce stress, improve overall well-being, and enhance the body’s ability to adapt to vestibular dysfunction.
Overall, the treatment options for vestibular nerve damage are diverse and aim to address the underlying causes, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life. A comprehensive approach that combines medical interventions, rehabilitation, and complementary therapies can provide the best outcomes for individuals with vestibular nerve damage.
Living with Vestibular Nerve Damage
Living with vestibular nerve damage can be a challenging experience that requires individuals to make certain lifestyle adjustments in order to minimize the impact of their symptoms. These adjustments can range from creating a safe and accessible environment to modifying daily activities and avoiding triggers that may exacerbate their condition. For example, individuals may need to rearrange furniture to create clear pathways and remove any potential hazards that could lead to falls. They may also need to install handrails or grab bars in their home to provide additional support and stability.
Modifying daily activities is another important aspect of managing vestibular nerve damage. This may involve making changes to one’s routine, such as taking breaks between activities to prevent fatigue and dizziness. It may also mean avoiding activities that involve rapid head movements, such as playing certain sports or riding roller coasters. By making these adjustments, individuals can reduce the risk of triggering their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Consulting with an occupational therapist can be incredibly beneficial for individuals with vestibular nerve damage. These professionals specialize in helping individuals adapt their living spaces to accommodate their specific needs. They can provide valuable guidance on how to make modifications that promote safety and accessibility, such as installing ramps or lifts for individuals with mobility challenges. Occupational therapists can also recommend assistive devices, such as canes or walkers, that can enhance stability and independence.
Coping Mechanisms and Support for Individuals with Vestibular Nerve Damage
Living with vestibular nerve damage can take a toll on an individual’s emotional well-being. It is important not to underestimate the impact that this condition can have on mental health. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, family, and support groups can provide reassurance and strategies for coping with the challenges that come with vestibular nerve damage.
Healthcare professionals, such as psychologists or counselors, can offer valuable guidance and support in managing the emotional aspects of living with vestibular nerve damage. They can help individuals develop coping mechanisms and provide strategies for managing anxiety or depression that may arise as a result of their condition. Additionally, they can assist individuals in navigating the complex emotions that often accompany chronic illnesses.
Support groups can also be a valuable resource for individuals with vestibular nerve damage. These groups provide a safe and understanding environment where individuals can share their experiences, learn from others, and gain a sense of community. Connecting with others who are going through similar challenges can be incredibly empowering and can help individuals feel less alone in their journey.
Practicing stress-management techniques can also play a significant role in improving overall well-being for individuals with vestibular nerve damage. Mindfulness and relaxation exercises, such as deep breathing or meditation, can help reduce stress and promote a sense of calm. Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as listening to music, reading, or spending time in nature, can also be beneficial in managing the emotional impact of vestibular nerve damage.
In conclusion, living with vestibular nerve damage requires individuals to make various lifestyle adjustments and seek support to manage their symptoms effectively. By creating a safe and accessible environment, modifying daily activities, and avoiding triggers, individuals can minimize the impact of their condition on their daily life. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, family, and support groups can provide valuable guidance and reassurance. Practicing stress-management techniques can also help improve overall well-being. It is important to remember that living with vestibular nerve damage requires patience, perseverance, and support from healthcare professionals and loved ones to navigate the physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges.
Remember, if you suspect you may have vestibular nerve damage, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.




+ There are no comments
Add yours