The vestibular nerve is a crucial component of our sensory system that plays a vital role in maintaining balance and spatial orientation. This nerve is responsible for transmitting information from the inner ear to the brain, allowing us to perceive and navigate our environment effectively. Understanding the intricacies of the vestibular nerve is essential for comprehending the impact it has on our daily lives and the potential disorders that can arise.
Understanding the Vestibular Nerve
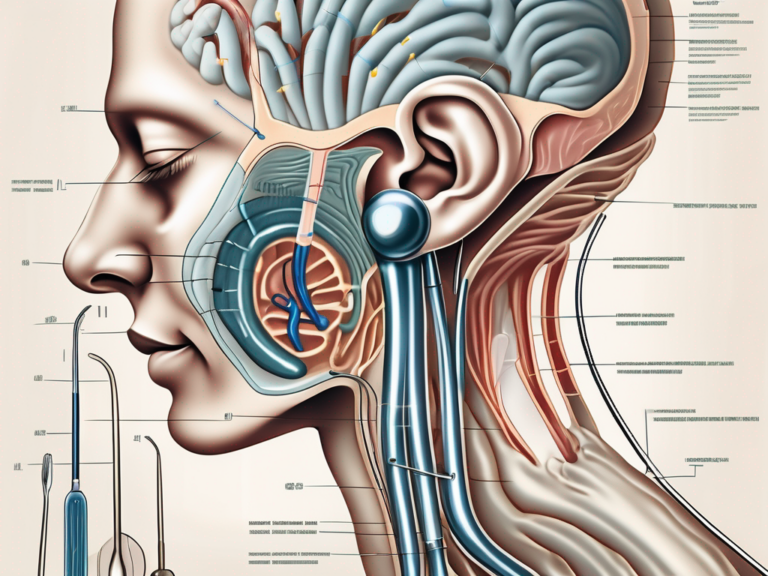
The vestibular nerve is a fascinating component of the human body’s intricate sensory system. It is one of the two branches of the vestibulocochlear nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve. This nerve plays a crucial role in our ability to maintain balance and spatial orientation.
Anatomy of the Vestibular Nerve
The vestibular nerve originates from the vestibular ganglion, which is located within the inner ear. This ganglion serves as a hub for the nerve fibers that make up the vestibular nerve. These fibers form a complex network that extends throughout the inner ear.
Within this network, the vestibular nerve receives sensory information from two main sources: the semicircular canals and the otolith organs. The semicircular canals detect rotational movements of the head, while the otolith organs sense linear acceleration and changes in head position.
Once the sensory information is collected, the vestibular nerve carries it to different areas of the brain, including the vestibular nuclei and the cerebellum. These regions are responsible for processing and integrating the sensory signals received from the vestibular nerve.
Function of the Vestibular Nerve
The vestibular nerve plays a vital role in relaying essential information about head movements, head position, and changes in acceleration and gravity to the brain. This information is crucial for maintaining balance and stability in various situations.
For example, when we walk or run, the vestibular nerve continuously provides feedback to the brain about the position and movement of our head. This feedback allows the brain to make rapid adjustments to our posture and muscle activity, ensuring that we stay upright and balanced.
Furthermore, the vestibular nerve contributes to our spatial orientation, enabling us to perceive our position in relation to the environment. This ability is particularly important when navigating through space, whether it’s walking through a crowded room or driving a car on a winding road.
The vestibular nerve works in close association with the visual system and other sensory inputs to provide a comprehensive understanding of our surroundings. By integrating information from multiple sources, our brain can create a coherent and accurate representation of the world around us.
In conclusion, the vestibular nerve is a remarkable component of our sensory system. Its intricate anatomy and crucial function in maintaining balance and spatial orientation make it an essential part of our everyday lives.
The Role of the Vestibular Nerve in Balance and Spatial Orientation
Connection between the Vestibular Nerve and the Brain
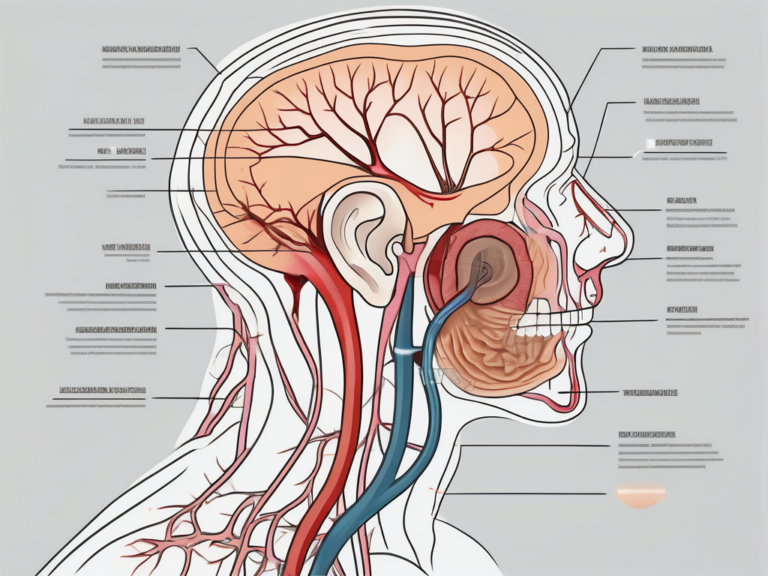
The vestibular nerve establishes a vital connection between the inner ear and the brain. It is a complex network of nerve fibers that play a crucial role in maintaining our balance and spatial orientation. Without the vestibular nerve, our ability to navigate the world around us would be severely compromised.
Within the brainstem, specifically in the vestibular nuclei, the information from the vestibular nerve is received and processed. These nuclei act as relay stations, ensuring that the signals are properly interpreted and sent to different areas of the brain. The processed signals are then transmitted to the cerebellum and various cortical regions, where they are further analyzed and integrated with other sensory inputs.
This intricate network allows for the coordination of motor responses that help maintain balance and stability. When we encounter a sudden shift in our body position or experience a change in our head movement, the vestibular nerve quickly detects these changes and sends signals to the brain. These signals trigger appropriate motor responses, such as adjusting our posture or activating specific muscles, to counteract the imbalance and keep us steady.
Furthermore, the vestibular nerve contributes to our perception of spatial orientation. It works in tandem with the visual system to enable accurate spatial perception and depth perception. This coordination between sensory inputs allows us to accurately judge distances, perceive the three-dimensional nature of our surroundings, and navigate through complex environments.
How the Vestibular Nerve Affects Movement and Perception
The information transmitted by the vestibular nerve has a profound impact on our movement and perception. It plays a crucial role in our ability to perform everyday tasks that require coordination and balance.
When the head moves or changes position, the vestibular nerve detects these changes and sends signals to the brain. These signals are then used to trigger appropriate motor responses, ensuring that we maintain our balance and adjust our body posture accordingly. For example, if we suddenly tilt our head to one side, the vestibular nerve will detect this change and send signals to activate the muscles in our neck and spine, allowing us to maintain an upright position.
Moreover, the vestibular nerve works in conjunction with the visual system to enable accurate spatial perception and depth perception. This coordination between sensory inputs allows us to accurately reach for objects, grasp them with precision, and navigate through complex environments without stumbling or falling.
Imagine walking on a narrow, winding path with uneven terrain. As you navigate through this challenging environment, your vestibular nerve is constantly sending signals to your brain, providing information about your body’s position and movement. This information is then integrated with visual cues, such as the distance and position of objects in your surroundings, to help you maintain your balance and adjust your movements accordingly.
In addition to its role in motor control and spatial perception, the vestibular nerve also contributes to our overall sense of well-being. It helps regulate our sense of dizziness and nausea, especially in situations where there is a mismatch between visual and vestibular inputs, such as when we are in a moving vehicle or on a roller coaster.
In conclusion, the vestibular nerve is a crucial component of our sensory system, playing a fundamental role in maintaining our balance, coordinating our movements, and providing us with a sense of spatial orientation. Its intricate connection with the brain allows for the integration of sensory inputs and the generation of appropriate motor responses. Without the vestibular nerve, our ability to navigate the world and interact with our surroundings would be greatly impaired.
Disorders Related to the Vestibular Nerve
The vestibular nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining our sense of balance and spatial orientation. When this nerve is affected by certain disorders, it can lead to a variety of symptoms that can greatly impact an individual’s daily life.
Symptoms of Vestibular Nerve Disorders
Vestibular nerve disorders can manifest in various ways, and individuals may experience a range of symptoms. These can include dizziness, vertigo, imbalance, nausea, difficulty concentrating, and even hearing loss. Each individual’s experience may differ, and it is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other factors.
When someone experiences these symptoms, it can be incredibly unsettling and disruptive. Simple tasks like walking or driving may become challenging, and the fear of falling or losing control can be overwhelming. The constant feeling of dizziness or vertigo can make it difficult to focus on daily activities, leading to frustration and a decreased quality of life.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in vestibular disorders. They can conduct a thorough examination and offer appropriate guidance based on your specific circumstances.
Common Vestibular Nerve Disorders
There are several common vestibular nerve disorders that can affect individuals of all ages. One such example is vestibular neuritis, which is often caused by a viral infection and leads to inflammation of the vestibular nerve. This condition can result in severe dizziness, vertigo, and a loss of balance.
Imagine waking up one morning and feeling an intense spinning sensation every time you try to move your head. This is what individuals with vestibular neuritis often experience. The inflammation of the vestibular nerve disrupts the signals sent to the brain, causing a profound sense of dizziness and disorientation. Simple tasks like standing up or turning your head can become incredibly challenging and may require assistance.
Another commonly encountered disorder is Meniere’s disease, characterized by recurring episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the affected ear. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and require effective management strategies.
Living with Meniere’s disease can be incredibly challenging. The sudden onset of vertigo can be debilitating, causing individuals to lose their balance and experience severe nausea. The accompanying hearing loss and tinnitus can further exacerbate the difficulties faced by those with this disorder. Simple tasks like attending social gatherings or enjoying music can become overwhelming and may require adjustments to accommodate the symptoms.
Managing these vestibular nerve disorders often involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Individuals may need to make changes to their daily routines, such as avoiding triggers that worsen their symptoms or incorporating exercises that help improve balance and stability.
It is important to remember that each individual’s experience with vestibular nerve disorders is unique, and treatment plans may vary accordingly. With the help of healthcare professionals specializing in vestibular disorders, individuals can find ways to manage their symptoms and regain control over their lives.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Vestibular Nerve Disorders
Vestibular nerve disorders can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, causing symptoms such as dizziness, vertigo, and imbalance. Accurate diagnosis and effective treatment are crucial for managing these conditions and improving daily functioning.
Diagnostic Procedures for Vestibular Nerve Disorders
Healthcare professionals specializing in vestibular disorders employ various diagnostic procedures to accurately assess the function of the vestibular system and identify any underlying pathology or abnormalities.
One of the initial steps in the diagnostic process is a detailed medical history review. This allows healthcare professionals to gather information about the patient’s symptoms, their duration and frequency, and any potential triggers or exacerbating factors. A thorough understanding of the patient’s medical history can provide valuable insights into the possible causes of their vestibular nerve disorder.
Physical examination is another essential component of the diagnostic process. Healthcare professionals may perform a series of tests to assess the patient’s balance, coordination, and eye movements. These tests can help identify any physical abnormalities or signs of vestibular dysfunction.
In addition to the medical history review and physical examination, specialized tests may be conducted to further evaluate the vestibular system. Videonystagmography (VNG) is a commonly used test that measures eye movements to assess the function of the vestibular system. This test can help identify specific abnormalities or weaknesses in the vestibular nerve.
Vestibular function tests are also employed to evaluate the patient’s balance and vestibular function. These tests may involve the use of computerized systems that measure the patient’s response to various stimuli, such as changes in head position or visual cues. By analyzing the patient’s responses, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into the nature and severity of their vestibular nerve disorder.
By combining the information gathered from the medical history review, physical examination, and specialized tests, healthcare professionals can make an accurate diagnosis of the vestibular nerve disorder. This diagnosis serves as the foundation for developing an individualized treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Vestibular Nerve Disorders
The treatment of vestibular nerve disorders is tailored to the underlying cause and the impact on an individual’s daily functioning. A personalized approach ensures the most effective management of symptoms and improved quality of life.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms during acute episodes. Anti-nausea drugs can help reduce feelings of nausea and vomiting, while vestibular suppressants can help alleviate dizziness and vertigo. These medications provide temporary relief and are typically used in conjunction with other treatment modalities.
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) is a specialized form of physical therapy that has shown great success in managing vestibular nerve disorders. This therapy focuses on exercises and maneuvers designed to improve balance, reduce dizziness, and enhance adaptation to sensory input.
VRT may include exercises that target specific components of the vestibular system, such as gaze stabilization exercises or balance training. These exercises aim to retrain the brain to compensate for any vestibular dysfunction and improve overall balance and coordination.
Furthermore, lifestyle modifications and self-care strategies can play a significant role in managing vestibular nerve disorders. Patients may be advised to make changes to their diet, avoid triggers that worsen symptoms, and incorporate stress management techniques into their daily routine.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional specializing in vestibular disorders to determine the most appropriate treatment options for your specific condition. They will consider factors such as the underlying cause of your vestibular nerve disorder, the severity of your symptoms, and your individual goals and preferences.
By working closely with healthcare professionals and following a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with vestibular nerve disorders can experience significant improvements in their symptoms and overall quality of life.
The Impact of Vestibular Nerve Disorders on Daily Life
Coping with Vestibular Nerve Disorders
Vestibular nerve disorders can significantly impact daily life, leading to difficulties in performing routine tasks and affecting overall well-being. Coping with these challenges requires patience, understanding, and support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends.
Vestibular nerve disorders can manifest in various ways, such as dizziness, vertigo, and imbalance. These symptoms can make it challenging for individuals to engage in activities that were once effortless, such as walking, driving, or even simply getting out of bed. The constant feeling of being off-balance can lead to frustration, anxiety, and a loss of confidence.
Simple adjustments to daily routines, such as taking breaks when symptoms worsen or modifying the environment to reduce fall risks, can significantly ease the burden. For example, installing handrails in the bathroom or using non-slip mats can help prevent accidents. Additionally, stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, can help individuals cope with the emotional and physical impact of vestibular nerve disorders.
Support from healthcare professionals is crucial in managing vestibular nerve disorders. They can provide guidance on specific exercises and activities that can improve balance and coordination. Physical therapists specializing in vestibular rehabilitation therapy can design personalized treatment plans to address individual needs.
Rehabilitation and Recovery from Vestibular Nerve Disorders
Rehabilitation plays a vital role in the recovery process for individuals with vestibular nerve disorders. Vestibular rehabilitation therapy, as mentioned earlier, can aid in the adaptation and compensation for the altered sensory input.
This form of therapy typically involves a series of exercises and activities aimed at retraining the brain to process sensory information more effectively and improve balance and coordination. These exercises may include head movements, eye exercises, and balance training. With time and dedication, many individuals can experience significant improvements in their symptoms and regain their functional abilities.
It is important to note that the recovery process may vary for each individual. Some may experience rapid improvements, while others may require more time and effort. Patience and perseverance are key during the rehabilitation journey.
Aside from physical rehabilitation, emotional support is also essential. Dealing with a vestibular nerve disorder can be emotionally challenging, and individuals may experience feelings of frustration, sadness, or isolation. Joining support groups or seeking counseling can provide a safe space to share experiences and learn coping strategies from others who are going through similar situations.
In conclusion, the vestibular nerve is a remarkable component of our sensory system that contributes to balance, spatial orientation, and movement. Understanding its anatomy, function, and connection to the brain provides valuable insights into the impact of vestibular nerve disorders. Seeking proper diagnosis and treatment from healthcare professionals specializing in vestibular disorders is crucial for managing symptoms effectively. While living with vestibular nerve disorders can present challenges, adopting coping strategies, engaging in rehabilitation, and seeking emotional support can enhance overall well-being and promote recovery.


+ There are no comments
Add yours