The vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve or the acoustic vestibular nerve, plays a crucial role in maintaining our balance and spatial orientation. Any form of damage to this nerve can have significant implications on our daily lives, as it can lead to a range of debilitating symptoms. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of vestibular nerve damage, including its anatomy and function, common causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Understanding the Vestibular Nerve
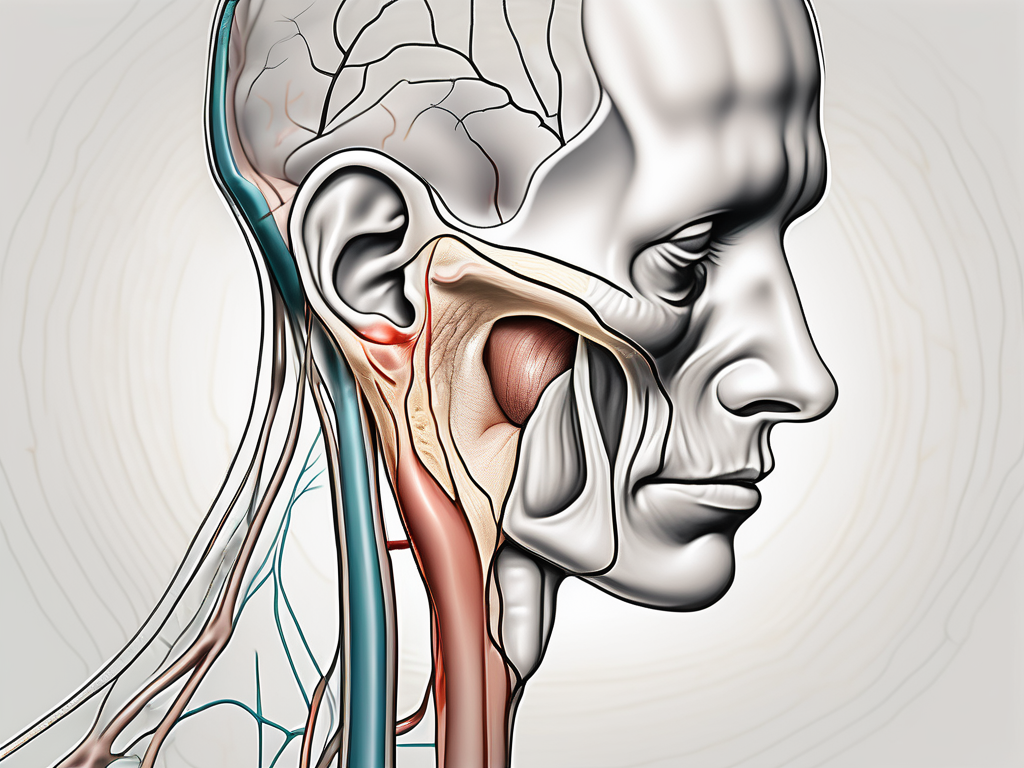
The vestibular nerve is a component of the vestibulocochlear nerve, which is responsible for transmitting sound and balance information from the inner ear to the brain. This nerve consists of two branches, the superior and inferior vestibular branches, both of which provide critical input to our vestibular system.
Anatomy of the Vestibular Nerve
The vestibular nerve originates from the vestibular ganglion, which is located within the inner ear. This ganglion is a cluster of nerve cell bodies that serve as the starting point for the vestibular nerve’s journey. From there, the vestibular nerve branches out into the semicircular canals, utricle, and saccule, which are crucial structures involved in detecting changes in head position and acceleration.
The semicircular canals, three fluid-filled tubes positioned at right angles to each other, play a significant role in our sense of rotational movement. When we turn our heads, the fluid inside these canals moves, stimulating hair cells that are responsible for detecting the movement. This information is then transmitted through the vestibular nerve to the brain, allowing us to perceive and adjust to changes in our orientation.
The utricle and saccule, on the other hand, are responsible for detecting linear acceleration and changes in head position relative to gravity. These structures contain tiny calcium carbonate crystals called otoliths, which are embedded in a gelatinous substance. When we move or change positions, the otoliths shift, bending hair cells and generating electrical signals that are transmitted through the vestibular nerve to the brain.
Together, the semicircular canals, utricle, and saccule provide us with a comprehensive understanding of our body’s position and movement in space. These structures collectively enable us to maintain our balance and posture, making activities like walking, running, and even standing still possible.
Function of the Vestibular Nerve
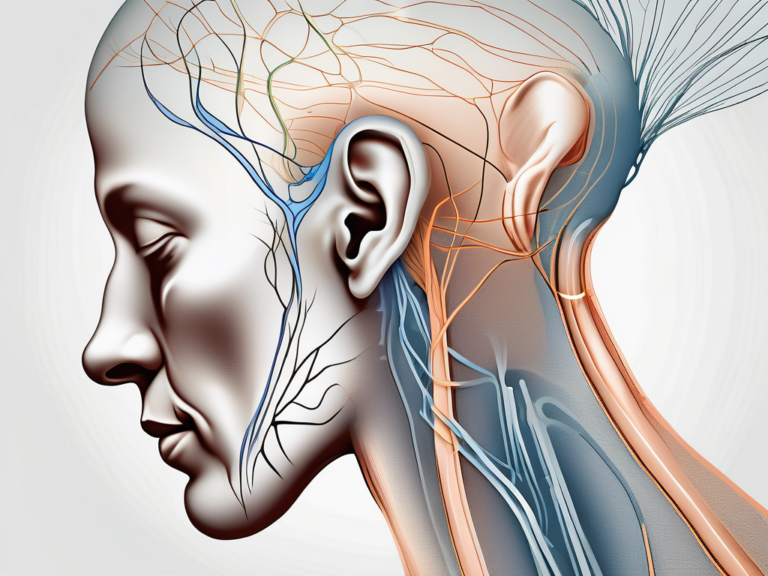
The vestibular nerve serves as a vital link between the inner ear and the brain. It carries sensory information related to head movements, gravitational forces, and spatial orientation. This information is crucial for our sense of balance and coordination.
When we move our heads, the fluid in the semicircular canals shifts, stimulating the hair cells and generating electrical signals. These signals are then transmitted through the vestibular nerve to the brainstem and cerebellum, where they are processed and integrated with information from other sensory systems, such as vision and proprioception.
The brainstem plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall balance and posture. It receives signals from the vestibular nerve and sends out commands to the muscles involved in maintaining stability. For example, if we tilt our head to one side, the brainstem will send signals to the muscles in our neck and back to adjust our posture and keep us upright.
The cerebellum, on the other hand, is responsible for fine-tuning our movements and coordinating them with our sense of balance. It receives information from the vestibular nerve and uses it to make precise adjustments to our posture and movements. This allows us to navigate our surroundings with ease and perform complex motor tasks with accuracy.
Overall, the vestibular nerve plays a crucial role in our ability to maintain stability and navigate our surroundings. Without this nerve and the information it provides, our sense of balance and coordination would be severely compromised, making even simple tasks challenging to perform.
Common Causes of Vestibular Nerve Damage
Vestibular nerve damage can occur due to various factors, including physical trauma, infections, and exposure to loud noises. Understanding these causes can help individuals take preventive measures or seek timely medical intervention when necessary.
Physical Trauma and Injuries
Head injuries, such as concussions or skull fractures, can potentially damage the vestibular nerve. These injuries may occur as a result of falls, accidents, or sports-related mishaps. It is crucial to always prioritize safety precautions and minimize the risk of head trauma.
When a person experiences a head injury, the impact can disrupt the delicate structures of the inner ear, including the vestibular nerve. The force from the injury can cause the nerve fibers to tear or become compressed, leading to vestibular dysfunction. This dysfunction can result in symptoms such as dizziness, vertigo, and imbalance.
Rehabilitation and physical therapy are often recommended for individuals with vestibular nerve damage caused by physical trauma. These therapies focus on improving balance, reducing dizziness, and restoring normal function to the vestibular system. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair severe nerve damage.
Infections and Diseases
Certain infections and diseases can also affect the vestibular nerve. Conditions like labyrinthitis, which is an inflammation of the inner ear, and vestibular neuritis, which is the inflammation of the vestibular nerve itself, can cause significant damage. Prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment can help mitigate the impact of such conditions.
Labyrinthitis is often caused by viral or bacterial infections that spread to the inner ear. The inflammation can disrupt the normal functioning of the vestibular nerve, leading to symptoms such as severe vertigo, nausea, and hearing loss. Treatment for labyrinthitis typically involves antibiotics or antiviral medications to combat the underlying infection, along with medications to alleviate symptoms.
Vestibular neuritis, on the other hand, is commonly caused by a viral infection, such as the herpes virus. The inflammation of the vestibular nerve can result in sudden and severe vertigo, accompanied by nausea and difficulty maintaining balance. Treatment for vestibular neuritis may include medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms, as well as vestibular rehabilitation therapy to aid in recovery.
Exposure to Loud Noises
Continuous exposure to loud noises, such as those experienced in industrial occupations or through recreational activities like attending loud concerts, can potentially harm the vestibular nerve. Wearing protective ear gear, reducing exposure to loud sounds, and taking regular breaks can help prevent such damage.
The vestibular nerve can be affected by prolonged exposure to loud noises, leading to a condition known as noise-induced vestibular dysfunction. This occurs when the sensory cells in the inner ear, including those connected to the vestibular nerve, are damaged by loud sounds. Symptoms may include dizziness, imbalance, and difficulty concentrating.
Prevention is key when it comes to protecting the vestibular nerve from noise-induced damage. Using earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments, keeping the volume at a reasonable level when using headphones or earphones, and taking regular breaks from loud activities can all help safeguard the vestibular system.
Symptoms of Vestibular Nerve Damage
Balance and Coordination Issues
One of the primary symptoms of vestibular nerve damage is a disruption in balance and coordination. Individuals may experience unsteadiness, dizziness, and an increased risk of falls. Simple tasks that were once effortless, such as walking or climbing stairs, may become challenging and anxiety-inducing.
This loss of balance and coordination can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life. Imagine trying to navigate through a crowded grocery store, constantly feeling like the ground beneath you is shifting. It can be incredibly frustrating and isolating.
Individuals with vestibular nerve damage may find themselves avoiding certain activities or places that they once enjoyed. The fear of falling or feeling dizzy can lead to a loss of independence and a decrease in overall quality of life.
Hearing Loss and Tinnitus
Vestibular nerve damage can also manifest as hearing impairments. Individuals may notice a reduction in their hearing capabilities or a persistent ringing or buzzing sensation in their ears, known as tinnitus. It is essential to seek professional evaluation and not dismiss these symptoms as mere inconveniences.
Hearing loss can have a profound impact on a person’s ability to communicate and engage with the world around them. Conversations may become difficult to follow, and social interactions can become exhausting as individuals struggle to hear and understand what is being said.
Tinnitus, on the other hand, can be incredibly distracting and disruptive. Imagine trying to concentrate on a task or enjoy a peaceful moment when there is a constant buzzing or ringing sound in your ears. It can be maddening and significantly impact a person’s mental well-being.
Cognitive and Emotional Effects
Furthermore, vestibular nerve damage can have psychological ramifications. Some individuals may experience difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and emotional disturbances such as anxiety or depression. It is crucial to address these effects holistically, with the support of medical professionals and appropriate therapeutic interventions.
The cognitive effects of vestibular nerve damage can make even the simplest tasks feel overwhelming. Concentration becomes a challenge as individuals struggle to stay focused amidst the constant dizziness and disorientation. Memory problems may arise, leading to frustration and a sense of helplessness.
Emotionally, vestibular nerve damage can take a toll on a person’s mental well-being. Anxiety and depression are common, as individuals grapple with the physical limitations and the impact it has on their daily lives. It is important for individuals to seek support from healthcare professionals who can provide guidance and help manage these emotional effects.
Living with vestibular nerve damage is not easy, but with the right support and interventions, individuals can find ways to manage their symptoms and regain a sense of control over their lives.
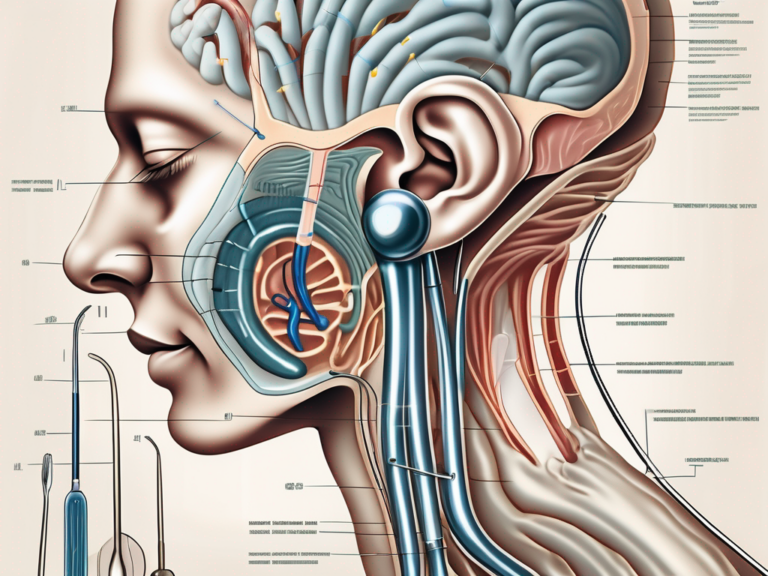
Diagnosis of Vestibular Nerve Damage
Medical History and Physical Examination
Diagnosing vestibular nerve damage typically involves a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s medical history and symptoms. A medical professional will perform a physical examination, including tests to assess balance, coordination, and eye movements. They may also inquire about any potential risk factors or incidents that might have contributed to the damage.
During the medical history assessment, the healthcare provider will ask detailed questions about the patient’s symptoms, such as dizziness, vertigo, and imbalance. They will also inquire about any previous ear infections, head trauma, or exposure to loud noises. This information is crucial in determining the possible causes of vestibular nerve damage.
The physical examination is an essential step in the diagnostic process. The healthcare provider will conduct a series of tests to evaluate the patient’s balance and coordination. These tests may include the Romberg test, which assesses the patient’s ability to maintain balance with their eyes closed, and the Fukuda-Unterberger test, which evaluates the patient’s ability to walk in a straight line without veering to one side.
In addition to balance and coordination tests, the healthcare provider will also examine the patient’s eye movements. Abnormal eye movements, such as nystagmus (involuntary eye movements), can indicate vestibular nerve damage. The healthcare provider may use a variety of techniques, including the Dix-Hallpike maneuver and the head impulse test, to assess the patient’s eye movements and determine the extent of the damage.
Imaging and Laboratory Tests
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary. These can include imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, to visualize the inner ear and related structures. These imaging tests provide detailed images of the vestibular system, allowing healthcare professionals to identify any structural abnormalities or tumors that may be causing the nerve damage.
During an MRI or CT scan, the patient lies on a table that slides into a large, tunnel-like machine. The machine uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the inner ear. These images can help healthcare professionals identify any abnormalities, such as inflammation, fluid buildup, or tumors, that may be affecting the vestibular nerve.
Laboratory tests, such as blood tests, may also help identify any underlying conditions that could be contributing to the nerve damage. For example, blood tests can detect infections, autoimmune disorders, or metabolic imbalances that may be affecting the vestibular system. These tests can provide valuable insights into the underlying cause of the nerve damage and guide the appropriate treatment plan.
In conclusion, the diagnosis of vestibular nerve damage involves a thorough medical history assessment, physical examination, and, in some cases, imaging and laboratory tests. These diagnostic tools help healthcare professionals identify the extent of the damage, determine the underlying cause, and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in managing vestibular nerve damage and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Treatment Options for Vestibular Nerve Damage
Vestibular nerve damage can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. While there is currently no cure for this condition, there are various treatment options available to help manage the symptoms effectively. These treatment options can range from medications and therapies to surgical interventions, as well as lifestyle changes and home remedies.
Medications and Therapies
One of the primary approaches to managing vestibular nerve damage is through the use of medications. Anti-vertigo or anti-nausea drugs can provide temporary relief from symptoms such as dizziness and nausea. These medications work by targeting the underlying causes of vestibular dysfunction, helping to alleviate the discomfort experienced by individuals with this condition.
In addition to medications, vestibular rehabilitation therapy is another effective treatment option. This therapy involves a series of exercises and maneuvers that aim to improve balance and reduce dizziness. These exercises are tailored to each individual’s specific needs and can be performed under the guidance of a trained physical therapist. Vestibular rehabilitation therapy has been shown to significantly enhance an individual’s ability to cope with the symptoms of vestibular nerve damage and improve their overall quality of life.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases of vestibular nerve damage or when other treatment options prove ineffective, surgical interventions may be considered. These surgical procedures can range from relatively simple interventions, such as decompressing the nerve or removing any growths that are compressing it, to more invasive procedures like vestibular neurectomy or cochlear implantation.
Vestibular neurectomy involves the surgical removal of the affected vestibular nerve, which can help alleviate symptoms such as vertigo and imbalance. This procedure is typically performed by a specialized surgeon and is only recommended after careful consideration and consultation with specialists.
Cochlear implantation, on the other hand, is a surgical procedure that involves the implantation of a device that stimulates the auditory nerve, bypassing the damaged vestibular nerve. This procedure is primarily used for individuals who have both vestibular and hearing loss, as it can help restore some level of hearing function while also addressing the vestibular symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
In addition to medical interventions, individuals with vestibular nerve damage can benefit from making certain lifestyle changes. Modifying the home environment to minimize fall risks is crucial, as individuals with vestibular dysfunction may be more prone to accidents and injuries. This can involve removing tripping hazards, installing handrails, and ensuring proper lighting throughout the home.
Implementing stress-reducing techniques can also be beneficial for individuals with vestibular nerve damage. Stress has been known to exacerbate symptoms such as dizziness and vertigo, so finding ways to manage stress levels can help alleviate these symptoms. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga can be effective in reducing stress and promoting overall well-being.
Furthermore, prioritizing regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet can contribute to the overall management of vestibular nerve damage. Engaging in exercises that focus on improving balance and coordination, such as tai chi or yoga, can be particularly beneficial. A well-balanced diet that includes foods rich in vitamins and minerals can also support the body’s natural healing processes.
It is important to note that before attempting any home remedies or making significant lifestyle changes, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice and guidance based on an individual’s specific condition and needs.
Prevention of Vestibular Nerve Damage
Protective Measures for the Ears
One of the best ways to prevent vestibular nerve damage is by taking appropriate measures to protect the ears. This includes wearing earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments, using headphones at lower volumes, and practicing caution when exposed to sudden or loud noises.
Regular Health Check-ups
Maintaining regular health check-ups with an audiologist or an ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialist can help identify potential problems before they escalate. These professionals can provide personalized advice based on an individual’s medical history and lifestyle, enabling them to take proactive steps to protect their vestibular nerve health.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Engaging in a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing stress levels, can also play a significant role in preventing vestibular nerve damage. These lifestyle choices contribute to overall well-being and can minimize the risk of various health issues, including those related to the vestibular system.
Conclusion
Damage to the vestibular nerve can disrupt our sense of balance, coordination, and overall quality of life. By understanding the anatomy and function of this crucial nerve, recognizing the common causes and symptoms of its damage, and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can enhance their chances of a successful recovery and better manage their symptoms. Remember, every case is unique, and it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to receive an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.


+ There are no comments
Add yours